About 40-80% of people complain of pain in the lumbar spine, but no more than 25% of them seek medical help. In fact, such unpleasant sensations can be caused by both relatively harmless reasons and pathological changes in the spine. Therefore, you should not treat them with contempt.
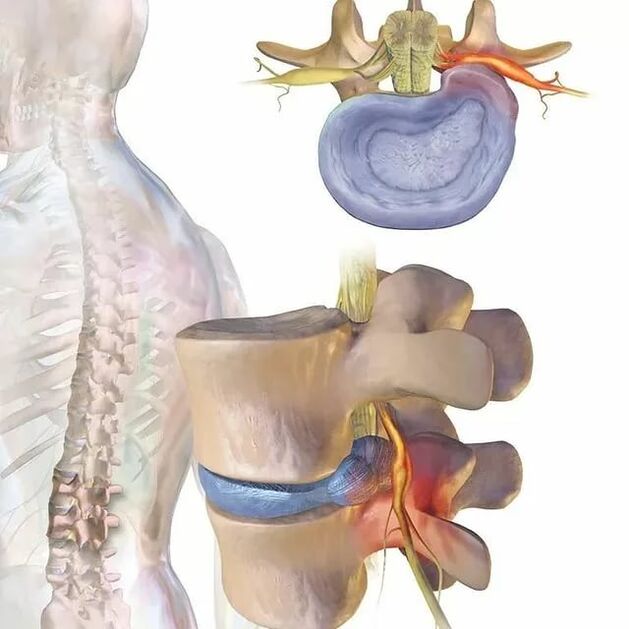
Causes of back pain
The spine consists of a complex whole of structural elements: bones, joints, discs, ligaments, nerves. Changes in any of them can be accompanied by painful sensations and are of a different nature. In addition, the spine is also surrounded by vertebrae muscles, the pain that patients often confuse with pain in the back spine. As such, the causes of the pain can be many. This can be due to overwork, the body's natural restructuring process during pregnancy, etc. v. But if the pain occurs frequently, you should contact a chiropractor or neurologist, since frequent pain in the spine in the lumbar region indicates the development of certain diseases. .
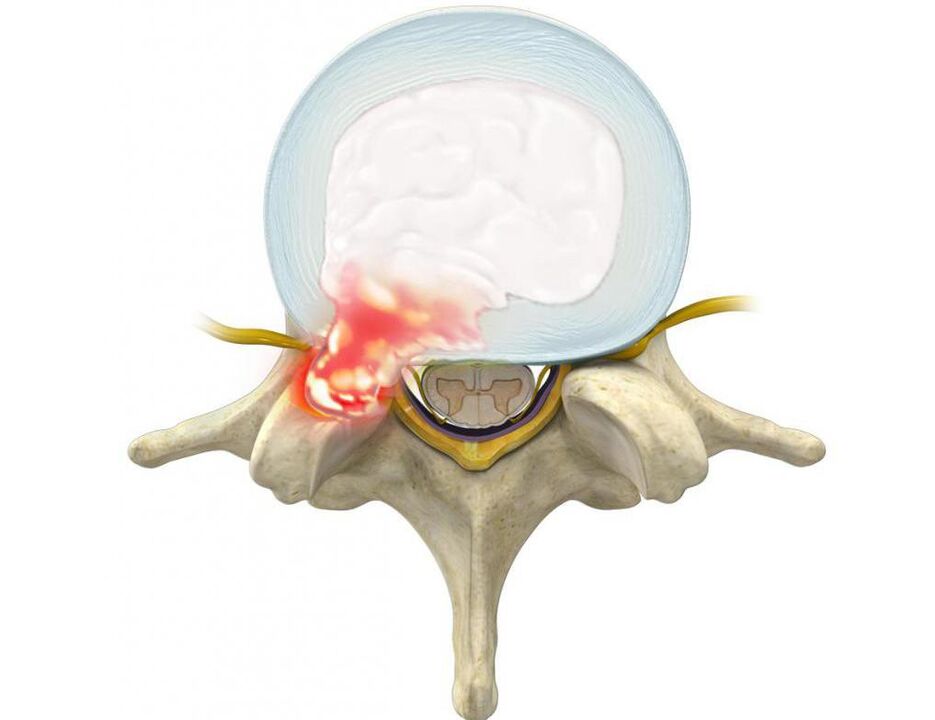
Usually, in such situations, the patient is diagnosed as:
- disc disease (decreased disc height, protrusion, disc herniation, discitis);
- facet joint pathologies (spondylolisthesis, joint cysts);
- inflammatory diseases (ankylosing spondylitis or ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis)
- Compression fractures of the vertebrae against the background of osteoporosis;
- neoplastic lesions of the spine.
Disc disease
Degenerative changes in the disc or osteonecrosis are very common, especially in young and middle-aged people. This is largely due to prolonged sitting or heavy physical labor. As we age, the discs dry out and the vertebrae grow together.
Already in the early stages of degenerative changes in the discs, which are special structural reservoirs that divide the vertebral bodies, pain in the spine can occur. This is due to irritation of the pain receptors of the outer layers of the discs, as well as the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Usually, osteonecrosis causes aseptic inflammation, which leads to reflex constriction of the segmental muscles. As a result, the pain in the spine increases, and at the same time, mobility is also limited.
Osteosarcoma tends to be progressive, especially in the absence of appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. It then leads to the formation of protrusions, and subsequently to herniated discs, exacerbation of existing symptoms and the emergence of new symptoms.
The lumbar region, because it is subjected to the highest loads during daily activities, is often affected the most.
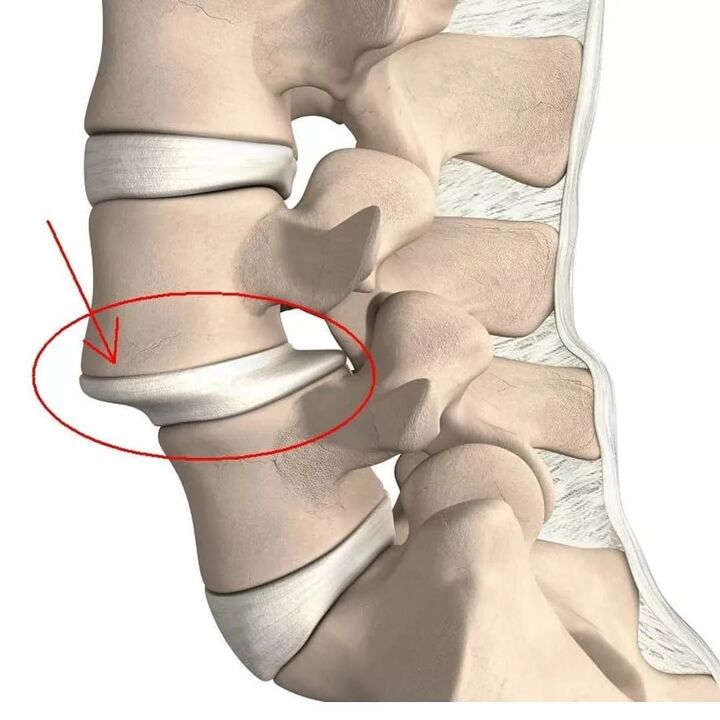
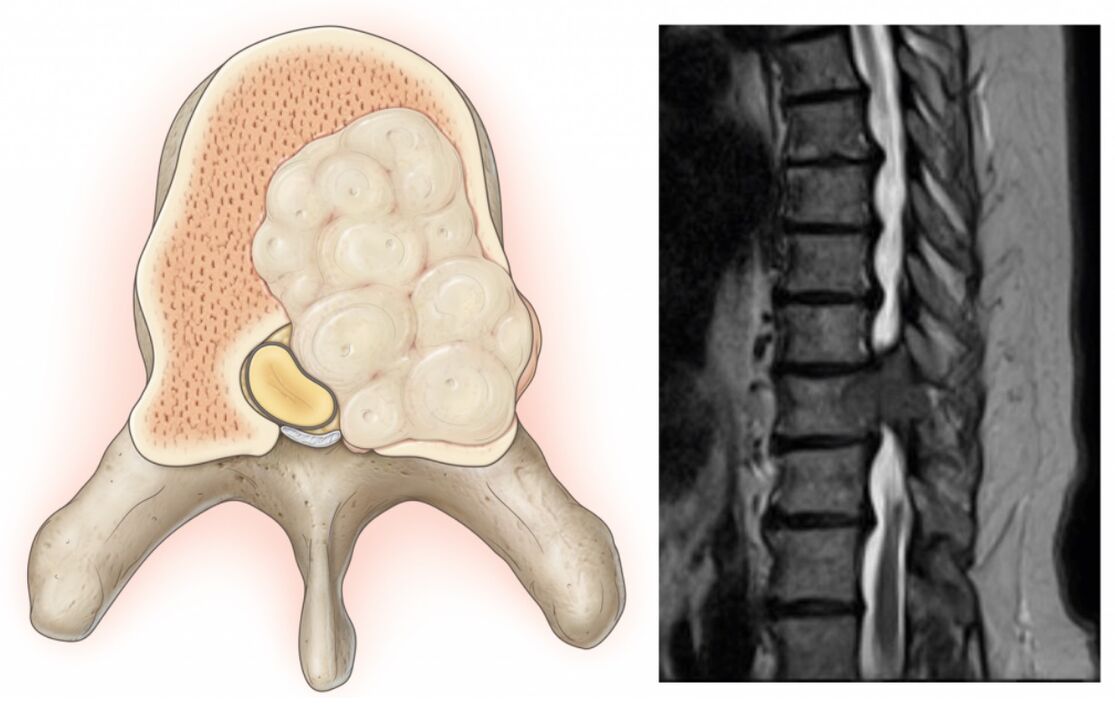
The protrusion is the protrusion of the disc while maintaining the integrity of its outer shell, known as the fibrous annular. While maintaining the effects of stimuli over time, the annulus fibers fail to withstand the load and pressure of the contents of the disc (medullary nucleus) and rupture. As a result, the nucleus extends beyond the physiological position of the disc. At the same time, the lumbar spine always hurts or the pain spreads to the legs, discomfort increases with sudden movements, bending, lifting heavy objects, stretching, coughing, sneezing, laughing, as well as when sitting for a long time. a position, walking, standing.
Often, patients with protrusion and hernia have unconsciously formed a forced posture, slightly leaning toward the healthy side. In this case, the pain in the lumbar spine can reach a high intensity, making the patient unable to work. In such cases, he is forced to adhere to bed rest, and to relieve pain, he squeezes the bent leg and brings it towards the abdomen.
Normally, protrusions and hernias form in the direction of the spinal canal, through which the spinal cord (cauda equina) and the nerve roots branching from it pass. The posterior portion passes through natural openings in the vertebral bodies and branches further into the lumbar plexus, responsible for the envelopment of the lower extremities and various organs (including the genitals). .
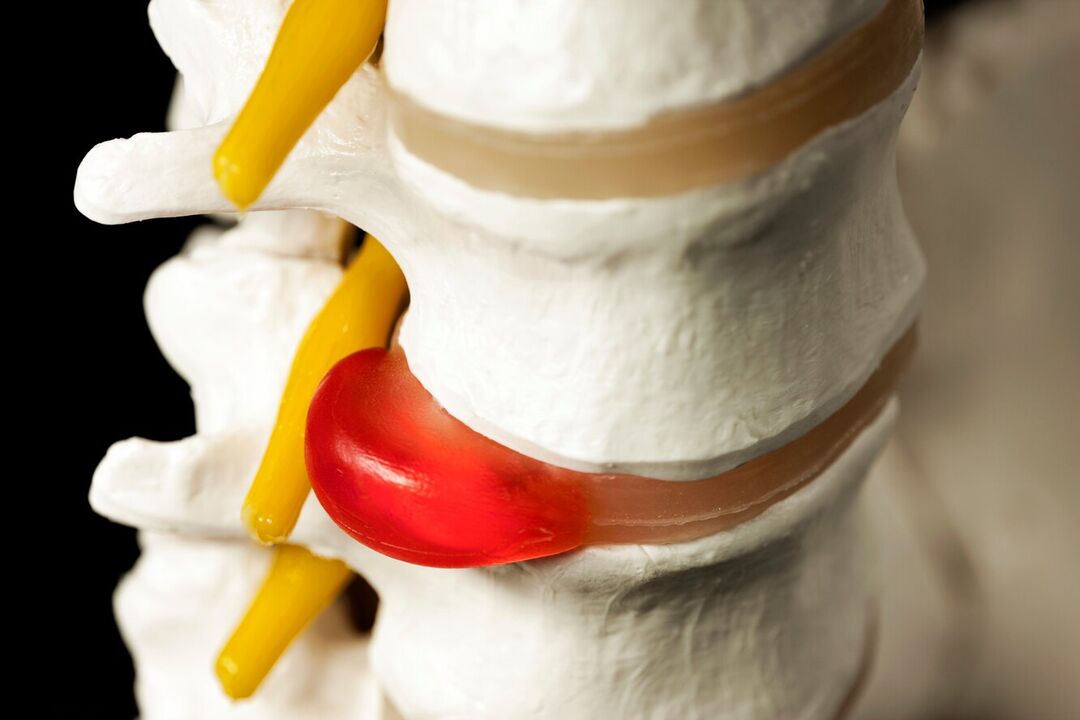
Therefore, often with long-term bone degeneration, formation of herniated masses in the lumbar region, gradual spinal pain is not only not rushed but also added other disorders. If the discs are deformed or the soft tissues are swollen from the inflammatory process that compresses the spinal roots that pass near them, neurological disorders will occur. Therefore, low back pain can be supplemented by radiating to the buttocks, groin, anterior, inner, outer thighs, lower legs, and feet. It depends on the type of nerve root that will be impaired, that is, to what extent pathological changes of the spinal motion segment will be observed. In addition, in the respective regions of the lower extremities, sensitization disturbances can be observed such as tingling sensation, numbness, changes in temperature sensitivity, pain, tactile stimulation, and limited motor ability. motion.
Changes in the height and function of the intervertebral discs that arise during osteochondrosis and its complications lead to damage to the articular apparatus of the spine, as well as degeneration of the vertebral bodies. The consequence of this is the development of spondylolisthesis, i. e. calcification of the anterior longitudinal ligament and the formation of cartilaginous growths on the surface of the vertebral body (osteocytes). Not only can they damage surrounding tissues and compress the spinal roots, causing severe pain in the spine, but they can also grow together. As a result, adjacent vertebral bodies are combined into a single whole, which significantly limits mobility in the lower back.
Osteoarthritis may be accompanied by reactive changes in the vertebral body, in particular, reactive aseptic spondylitis, leading to fibrosis. This is accompanied by compaction of bone tissue and greatly increases the likelihood of vertebral fractures.
Joint diseases
Pathologies of the facet joints or joints of the lumbar spine, especially their arthropathy, can also cause spinal pain in the lumbar region, including severe pain. Although more often, the pain is aching and localized deep within. Their appearance is due to the fact that their bursa is rich inside. In such situations, pain is often centered directly on the affected area and tends to increase with bending, stretching, turning, or standing for long periods of time. Walking and sitting help reduce their severity. But in some cases, pain can also appear in the groin, coccyx, back, and outer thighs.
Inflammatory diseases of the spine
Inflammatory diseases of the spine are less common than diseases of the discs and joints. However, they also cause damage to the spine. Including:
- ankylosing spondylitis or ankylosing spondylitis;
- reactive arthritis;
- psoriatic arthritis, etc. v.
Symptoms of these diseases usually occur before the age of 40, and more often by the age of 20. This distinguishes them from degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the discs and joints of the spine, which usually develop after 40 years. . In this case, the pain is characterized by a gradual increase in intensity. Furthermore, their severity decreased after exertion, but not at rest. Therefore, in inflammatory diseases, the lumbar spine often hurts at night and is especially strong in the morning, right after sleeping.
The most difficult situation is ankylosing spondylitis, and it is she who more often than other inflammatory diseases affect the lumbar region. This term means inflammation of the intervertebral disc joints with their subsequent fixation due to the formation of a fusion of solid bone, cartilage or fibers between the bony structures.
At first, the manifestation is mild back pain, but over time they spread higher and higher, covering the chest and then the cervical spine. This is associated with the development of limited mobility of the spine in all planes, since the spine, as a result of ongoing changes, appears to be sunken in a particular case. Also observed:
- alignment of lumbar pathology (natural curvature of the spine in the lumbar region);
- exacerbation of thoracic kyphosis, causing people to stoop;
- back stretch reflex;
- aggravation of mobility limitation due to the involvement of the facet joints in the pathological process and hardening of the disc;
- morning stiffness for an hour or more.
In 10-50% of patients, inflammation of the iris (iritis), cornea (keratitis), mucous membrane (conjunctivitis), iris, and ciliary body of the eyeball (iritis) can be observed. ).
The progression of ankylosing spondylitis leads to the fact that more and more joints in the pathological process. As a result, the patient is forced into a so-called begging position. It means a hunched thoracic spine, tilting the upper body downwards, bending the knees with a marked limitation of the range of motion of the ribcage, affecting the depth of breathing.
The rate at which the disease progresses depends on the appropriateness and adequacy of treatment.
Compression fracture vertebra
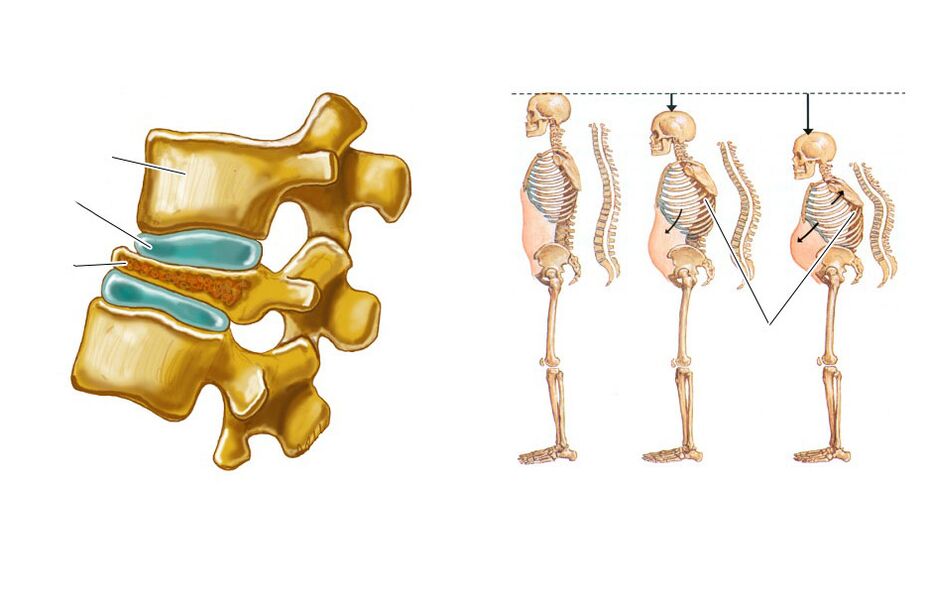
Compression fracture is the flattening of the vertebral body, so that it becomes wedge-shaped. This leads to disruption of the anatomical structure of the spine, which can cause trauma to the spinal cord and its roots, and also becomes a trigger for the rapid progression of degenerative changes-dystrophy.
Lumbar vertebrae 1 and 2 are more susceptible to injury, as they bear the greatest axial load.
Compression fractures commonly occur in the elderly due to the development of osteoporosis, i. e. decreased bone density. In such cases, to get injured, it can be not only a light fall, but also lifting weights, an unsuccessful move.
The disease is characterized by pain in the spine that limits movement, which increases when sitting, moving and trying to raise a straight leg. It usually lasts 1-2 weeks and then subsides over 2-3 months. In some cases, pain is present in the crest of the pelvis and hips. The decrease in height of the fractured vertebra causes an increase in lumbar pathology, which also contributes to the appearance of pain sensations.
If the fracture is not diagnosed in time, it will reduce the height of the vertebrae, leading to a change in posture and a decrease in growth rate. This causes reflex tension and shortens the muscles of the spine, causing chronic back pain and the need for long rest.
Spinal neoplasm injury
Neoplastic lesions of the spine mean the formation of benign and malignant tumors in which, as well as metastases, their origin are tumors of other organs. This is much less common than disc disease, facet joints, ankylosing spondylitis, and even compression fractures, specifically in only 1-2% of patients with back pain. But such lesions require diagnosis and treatment as early as possible.
Characteristic features of neoplastic lesions of the spine, in addition to pain sensation in it, are:
- an increase in body temperature, including values up to below the threshold;
- unreasonable weight loss;
- inability to find a comfortable body position;
- the presence of pain at night;
- severe pain in the spine;
- inability to relieve pain with conventional pain relievers.
Even if you have 1 or 2 of these symptoms, you should make an appointment with your doctor right away.
In a similar fashion, the following may appear:
- Chondroma is a malignancy diagnosed in 20% of patients with cancerous lesions of the spine. Usually it forms in the sacrum and can occur in people of all ages and genders.
- Young's sarcoma - occurs in 8% of patients with neoplastic lesions of the spine. More common in young men.
- Chondrosarcoma is a malignant cancer, accounting for 7-12% of cases. It is more commonly found in middle-aged men.
- Bone cysts are a type of benign tumor.
- A hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor present in 11% of people. It may go undetected during a person's lifetime. But it increases the risk of vertebral fractures.
- Metastases of other tumors are secondary malignancies. Usually, breast, prostate, lung, and less often kidney, thyroid, and skin cancers metastasize to the spine.
Diagnose
If the spine in the lumbar region is painful, you should make an appointment with a neurologist or chiropractor. At the appointment, the doctor initially collects a medical history, asking questions about the nature of the pain, the circumstances in which it occurred, how long it has persisted, the presence of other symptoms, lifestyle, and so on. . v.
The specialist then conducts an examination. Within its framework, he not only palpates the spine, determines the location of the pain, evaluates the gait and posture that the patient makes unconsciously, but also conducts functional tests. With their help, you can detect signs of ankylosing spondylitis, neurological deficits, assess spinal mobility and obtain other diagnostic data.
Based on this, the doctor was able to suggest possible causes of the pain syndrome. To clarify them, as well as to accurately determine the degree of damage, additional diagnostic and sometimes laboratory methods are prescribed. They often resort to help:
- radiographs in front and side projection, sometimes with functional radiological tests;
- CT - allows better visualization of bone structures, therefore, it is often used to diagnose spondylolisthesis, fracture, osteoma, etc. v. ;
- MRI - helps to evaluate the state of cartilage and soft tissue structures as carefully as possible, therefore it is often used to diagnose osteosarcoma, protrusion, herniated disc, spinal cord injury, etc. . v. ;
- electromyography - is indicated for neurological disorders of unknown etiology, as well as to assess the degree of nerve damage;
- radioisotope bone scan - used to diagnose malignancies and metastases;
- X-ray densitometry is the best method for diagnosing osteoporosis;
- myelography - used to detect the signs of compression of the spinal cord and nerves of the vertebral balance.
Treatment
For each patient, treatment is selected strictly on an individual basis, and not only on the basis of diagnosis but also on the nature of existing comorbidities. However, it is the cause of the back pain that determines the treatment tactics. It can be conservative or surgical intervention.
But the first step is always to direct pain relief efforts, especially if it's intense. For this, the patient is prescribed NSAIDs, antispasmodics, analgesics. And in severe cases, spinal blockade is done - injecting anesthetics and corticosteroids at specific points in the spine.
Bed rest is not shown to all patients. And with disc diseases, it can be completely contraindicated, because the reduction of physical activity contributes to the transformation of acute pain in the spine into chronic pain.
Conservative or non-surgical treatment is especially indicated for:
- bone necrosis;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- paresis of the facet joints;
- mild compression fracture.
It is often complex and includes:
- drug therapy, which may include NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids,
- physical therapy (UHF, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, traction therapy, etc. );
- Exercise therapy;
- manual therapy.

If the cause of back pain is herniated disc, condyle, spondylolisthesis, severe vertebral fracture, tumor, surgery is usually indicated. It is also needed for:
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy for degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- an increase in neurological deficits;
- instability of the spinal segment of motion;
- the development of complications, especially spinal stenosis.
Most modern spine surgeries are minimally invasive. As a result, the risks during and after surgery are sharply reduced, the rehabilitation time is shortened and more convenient, the effect is not inferior to open surgery with many injuries. Depending on the detected disease, it may be recommended:
- Surgical resection is a surgery indicated mainly for hernias and protrusions, especially those causing cauda equina syndrome. It can be performed with microsurgery through a 3 cm incision (microscopic excision) and using endoscopic equipment that feeds the spine through perforations approx. 1 cm (laparoscopic resection). When the disc is completely removed, it is usually replaced with an implant.
- Spondyloplasty and spondyloplasty - indicated for compression fractures of the vertebrae, hemangiomas and some other diseases. The essence of this operation is to deliver hard bone cement rapidly through a thin catheter into the vertebral body, which enhances its strength. With spondylolisthesis, it is also possible to restore the normal size of the vertebral body, which is important in cases of severe height loss due to fracture.
- Surgical immobilization is used to stabilize the spine. For this, metal structures of a different nature are used, which often remain in the patient's body until the end of life.
As a result, the spine in the lumbar region can be painful for a variety of reasons. Therefore, with persistent, persistent pain sensations, frequent occurrence, pain increasing over time and even additional symptoms, it is imperative to contact a chiropractor or a chiropractor. nerve. Early diagnosis helps to detect pathological changes at the most manageable stages, and if the disease is not completely cured, it should at least prevent progression and maintain a high standard of living.












































